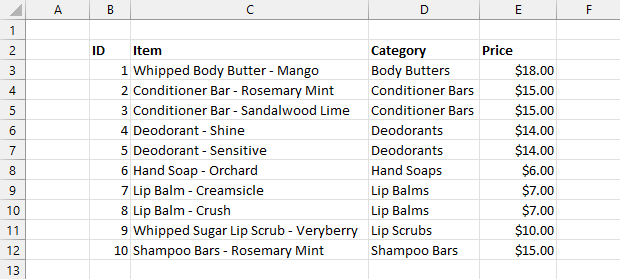
Do you want to make a table in Excel? This post is going to show you how to create a table from your Excel data.
Entering and storing data is a common task in Excel. If this is something you’re doing, then you need to use a table.
Tables are containers for your data! They help you keep all your related data together and organized.
Tables have a lot of great features and work well with other tools inside and outside of Excel, so you should definitely be using them with your data.
This post is going to show you all the ways you can create a table from your data in Excel. Get your copy of the example workbook used in this post and follow along!

Excel tables are the perfect container for tabular datasets due to their row and column structure. Just make sure your data follows these rules.
If your data is rectangular in shape and adheres to the above rules, then it’s ready to be put into a table.
Now that your data is ready to be placed inside a table, how can you do that?
It’s very easy and will only take a few clicks!
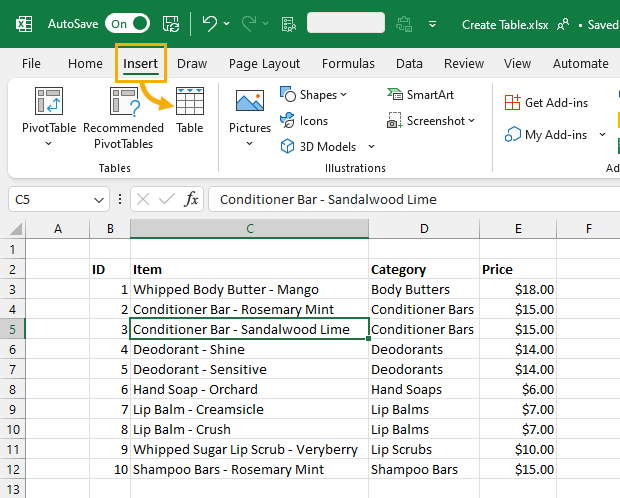
You’ll be able to add your data in a table from the Insert tab. Follow these steps to get your data into a table!
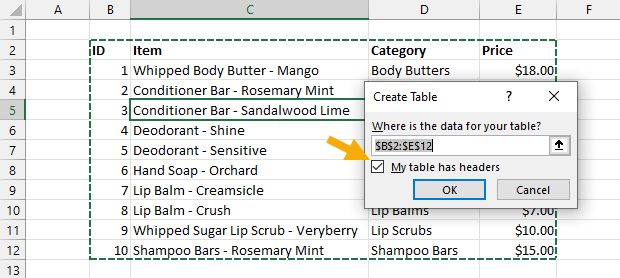
This is going to open the Create Table menu with your data range selected. You should see a green dash line around your selected data and you can adjust the selection if needed.
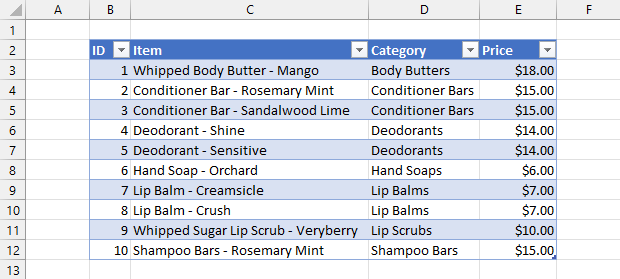
Your data is now inside a table! You’ll easily be able to tell the data is inside an Excel Table now because a default table formatting is automatically applied.
You can go to the Table Design tab and select other style options from the Table Styles section.
💡 Tip: Your table will get a default name such as Table1. You should give your new table a descriptive name as this is how you will refer to it in formulas and other tools.
Another place you can access the table command is from the Home tab.
You can use the Format as Table command to create a table.
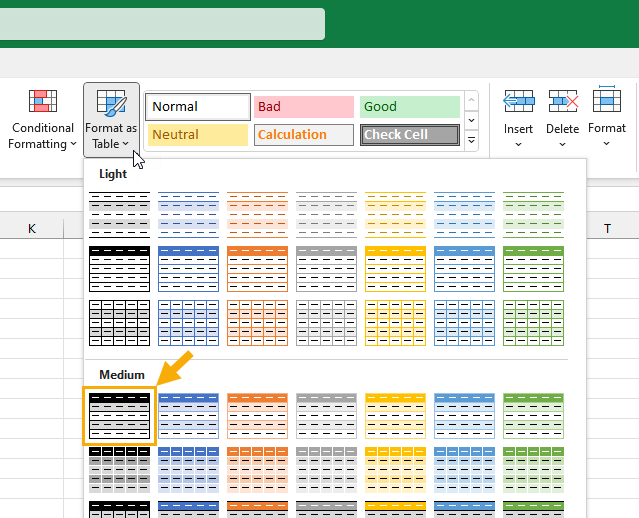
This is a great option as you get to choose the table style during the process of making your table.
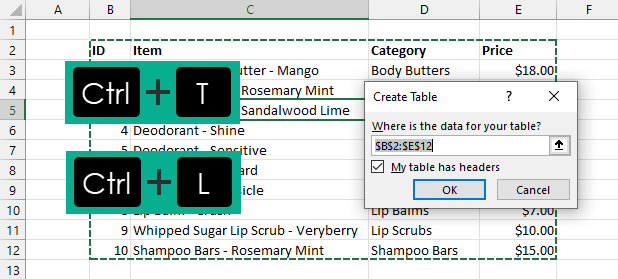
Creating a table is such a common task that there is a keyboard shortcut for it.
Select your data and press Ctrl + T on your keyboard to turn your dataset into a table.
This is an easy shortcut to remember since T stands for Table.
There is also a legacy shortcut available from when tables were called lists. Select your data and if you press Ctrl + L this will also make a table. In this case, L stands for List.
When you select any range Excel will show you the Quick Analysis options in the lower right corner.
This will give you quick access to conditional formatting, pivot tables, charts, totals, and sparklines. The menu also includes the table command to convert the data into a table.
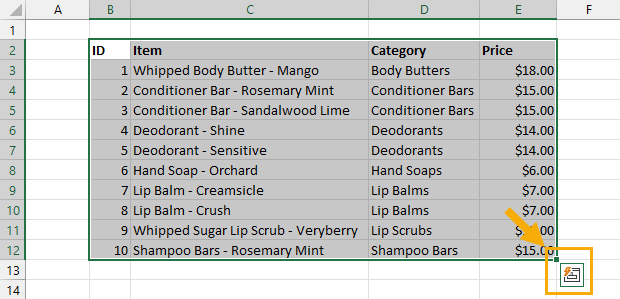
You can follow these steps to create a table from the Quick Analysis tools.
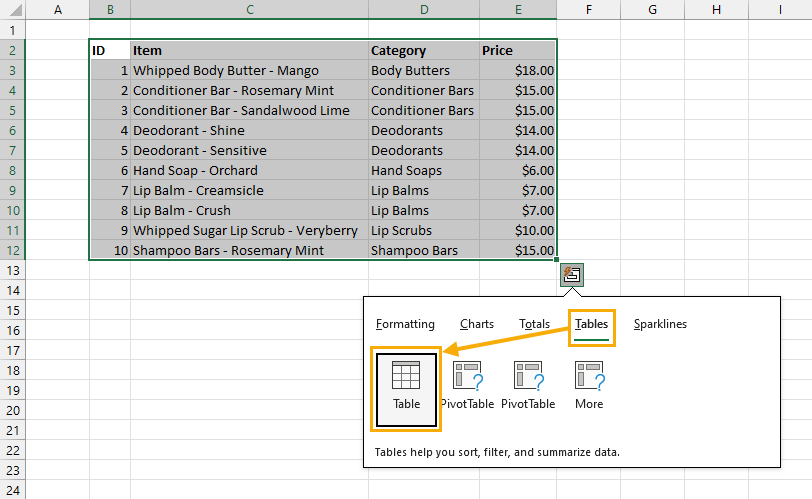
This should automatically show the Quick Analysis tool in the lower right corner of the selected range.
📝 Note: This method allows you to skip the Create Table menu and the Quick Analysis will guess if your data has column headings or not. Excel will apply any column headings to your table accordingly.
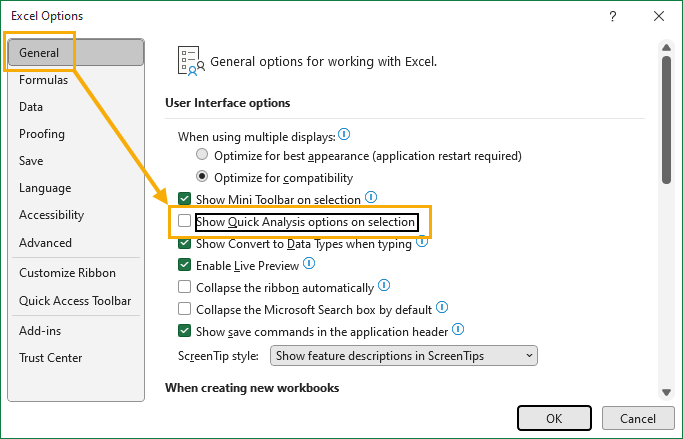
Quick Analysis can be disabled from the Excel Options menu if the pop-up command is something you find annoying.
📝 Note: This will only disable the small pop-up command from showing when you select your data. You can still use the Ctrl + Q keyboard shortcut to access the Quick Analysis tools for any selected range.
Power Query is a very useful tool for transforming your data, but you can also create a table during the process of building your queries.
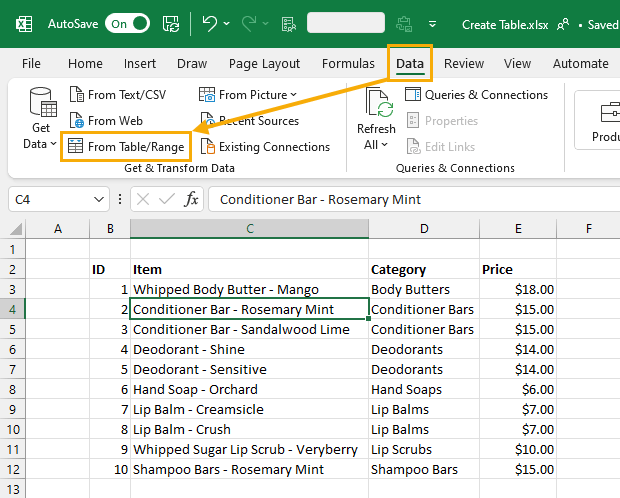
If your data isn’t already inside a table, you can use the From Table/Range query to make a table.
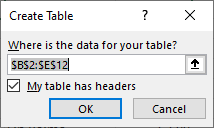
This will open the Create Table menu.
This will add your data to a table and then open the Power Query Editor where you will be able to build your query based on the new table.
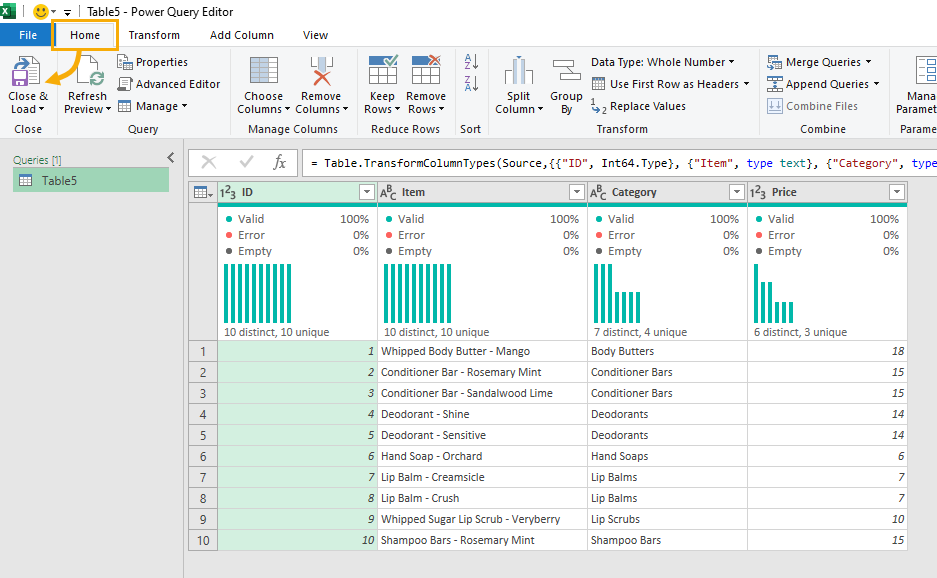
When you are finished building your query, you can go to the Home tab of the Power Query editor and press the Close and Load command.
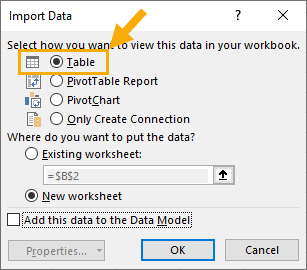
This will give you the option to create another table filled with the transformed data. Select the Table option and press the OK button to load the transformed data into a table.
⚠️ Warning: This method does create a table, but doesn’t give you the opportunity to name the table before you build your queries. This means your queries will reference the generic table name such as Table1, and if you later change the table name you will also have to update the reference in your query.
Suppose you need to create multiple tables in your Excel file. Maybe you need to create a table of sales data for each month of the year. Doing this manually could be a time-consuming process.
This is where you could use VBA to create multiple tables with the required columns.
Go to the Developer tab and select the Visual Basic command to open the visual basic editor. Then go to the Insert tab of the visual basic editor and select the Module option to create a new module to add your VBA macro.
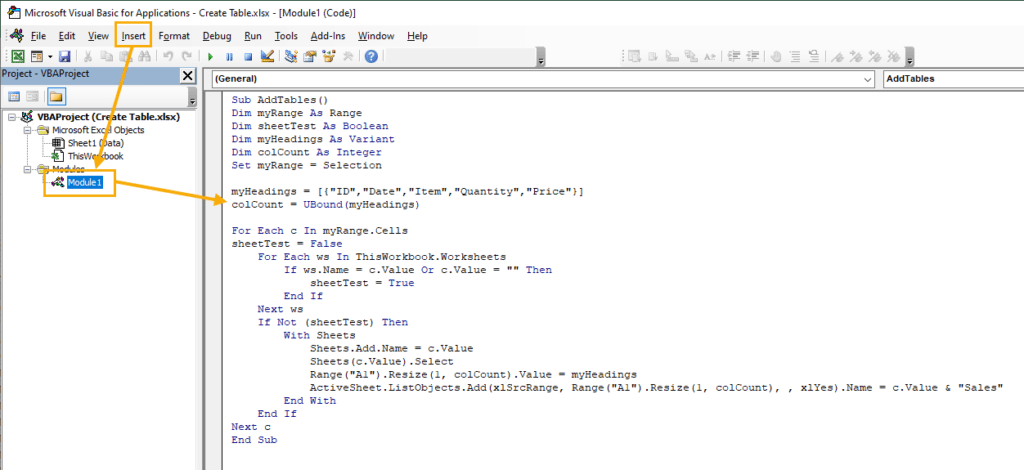
Sub AddTables() Dim myRange As Range Dim sheetTest As Boolean Dim myHeadings As Variant Dim colCount As Integer Set myRange = Selection myHeadings = [] colCount = UBound(myHeadings) For Each c In myRange.Cells sheetTest = False For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If ws.Name = c.Value Or c.Value = "" Then sheetTest = True End If Next ws If Not (sheetTest) Then With Sheets Sheets.Add.Name = c.Value Sheets(c.Value).Select Range("A1").Resize(1, colCount).Value = myHeadings ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range("A1").Resize(1, colCount), , xlYes).Name = c.Value & "Sales" End With End If Next c End SubThis code will loop through the selected range and add a new sheet for each cell in the range. The code tests if the sheet name exists and if it doesn’t then it creates a new sheet named from the cell value.
The column headings are added to the new sheet starting at cell A1. This is then turned into a table and the table is named based on the sheet name.
myHeadings = []The above line of code is used to create the column headings in each table. You can adjust this to suit your needs.
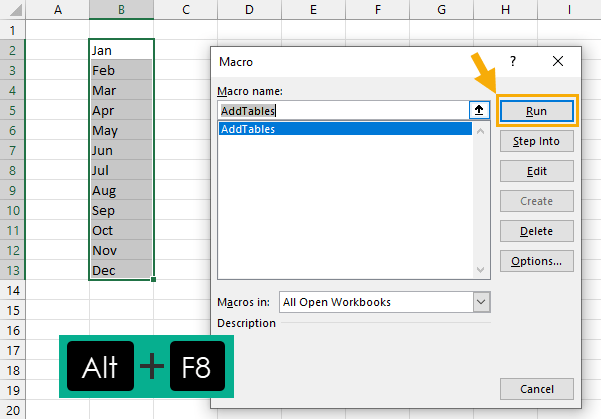
You can then run this macro to create multiple tables.
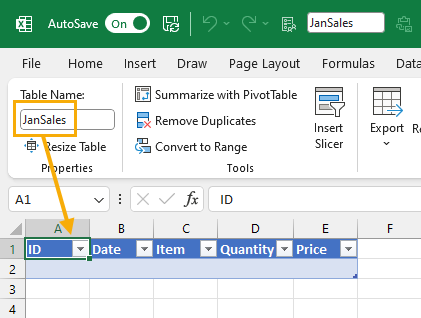
This will run and create a new sheet for each item in your selection. Each sheet will contain a table with the same column headings and be named based on the items in the selected list.
If you are using Excel online and want to automate the process of creating multiple tables from a list, then you will need to use Office Scripts.
This is a JavaScript based language that can help you automate tasks in Excel online.
Go to the Automate tab and select the New Script command to open the Office Script Editor.
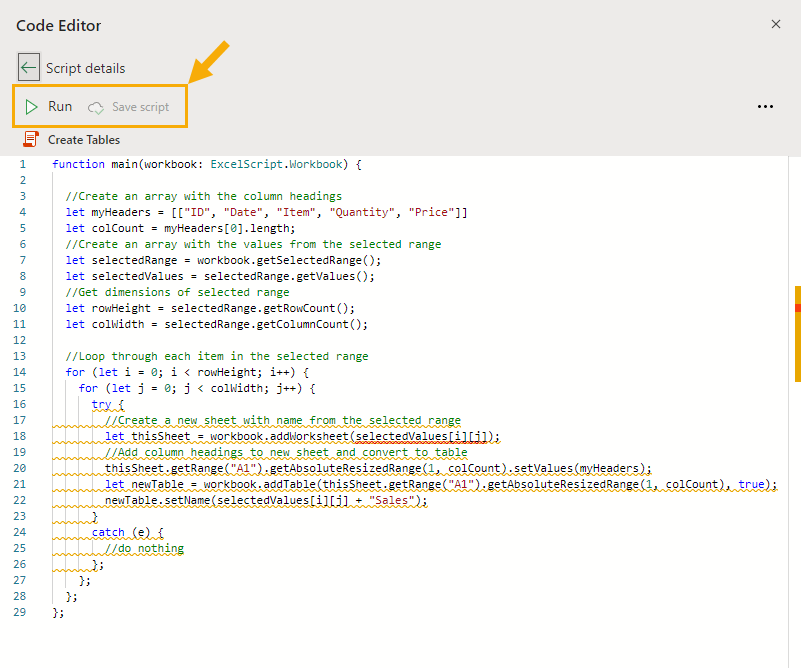
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) < //Create an array with the column headings let myHeaders = [["ID", "Date", "Item", "Quantity", "Price"]] let colCount = myHeaders[0].length; //Create an array with the values from the selected range let selectedRange = workbook.getSelectedRange(); let selectedValues = selectedRange.getValues(); //Get dimensions of selected range let rowHeight = selectedRange.getRowCount(); let colWidth = selectedRange.getColumnCount(); //Loop through each item in the selected range for (let i = 0; i < rowHeight; i++) < for (let j = 0; j < colWidth; j++) < try < //Create a new sheet with name from the selected range let thisSheet = workbook.addWorksheet(selectedValues[i][j]); //Add column headings to new sheet and convert to table thisSheet.getRange("A1").getAbsoluteResizedRange(1, colCount).setValues(myHeaders); let newTable = workbook.addTable(thisSheet.getRange("A1").getAbsoluteResizedRange(1, colCount), true); newTable.setName(selectedValues[i][j] + "Sales"); >catch (e) < //do nothing >; >; >; >;Copy and paste the above code into the Code Editor. Press the Save script button to save the script and then you can use the Run button to execute the script.
This Office Script code will loop through the active range in your workbook and create a new sheet for each cell in the selected range and name it based on the value in the cell.
let myHeaders = [["ID", "Date", "Item", "Quantity", "Price"]]The column headings are added to each new sheet starting in cell A1. You can adjust the above line of code to change the column headings to suit your needs.
These column headings are then turned into a table and the table is named based on the sheet name.
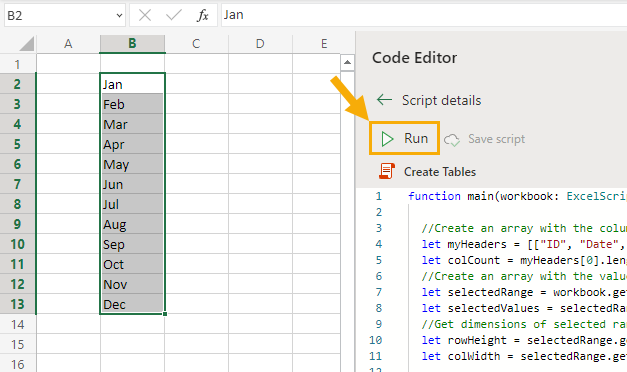
You can then run this script using the following steps.
The code will run and create all the sheets with tables in each sheet.
Tables are a very useful feature for your tabular data in Excel.
Your data can be added to a table in several ways such as from the Insert tab, from the Home tab, with a keyboard shortcut, or using the Quick Analysis tools.
Tables work well with other tools in Excel such as Power Query. Because of this, Excel will even automatically convert your data into a table before using Power Query.
Creating multiple tables in your workbook can also be automated using either VBA or Office Scripts.
How do you make your tables? Do you know any other tips? Let me know in the comments section below!
John is a Microsoft MVP and qualified actuary with over 15 years of experience. He has worked in a variety of industries, including insurance, ad tech, and most recently Power Platform consulting. He is a keen problem solver and has a passion for using technology to make businesses more efficient.
Subscribe for awesome Microsoft Excel videos 😃
👉 Find out more about our Advanced Formulas course!